By Clara Bird, Masters Student, OSU Department of Fisheries and Wildlife, Geospatial Ecology of Marine Megafauna Lab
Hi everyone! My name is Clara Bird and I am the newest graduate student in the GEMM lab. For my master’s thesis I will be using drone footage of gray whales to study their foraging ecology. I promise to talk about how cool gray whales in a following blog post, but for my first effort I am choosing to write about something that I have wanted to explain for a while: algorithms. As part of previous research projects, I developed a few semi-automated image analysis algorithms and I have always struggled with that jargon-filled phrase. I remember being intimidated by the term algorithm and thinking that I would never be able to develop one. So, for my first blog I thought that I would break down what goes into image analysis algorithms and demystify a term that is often thrown around but not well explained.
What is an algorithm?
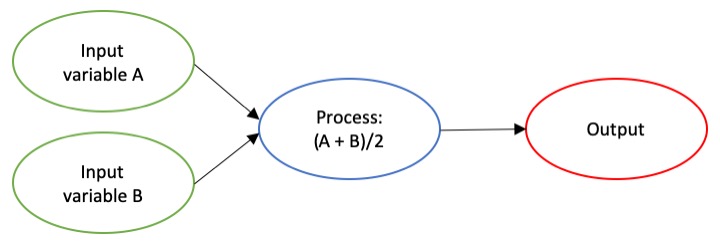
The dictionary broadly defines an algorithm as “a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem or accomplishing some end” (Merriam-Webster). Imagine an algorithm as a flow chart (Fig. 1), where each step is some process that is applied to the input(s) to get the desired output. In image analysis the output is usually isolated sections of the image that represent a specific feature; for example, isolating and counting the number of penguins in an image. Algorithm development involves figuring out which processes to use in order to consistently get desired results. I have conducted image analysis previously and these processes typically involve figuring out how to find a certain cutoff value. But, before I go too far down that road, let’s break down an image and the characteristics that are important for image analysis.
What is an image?
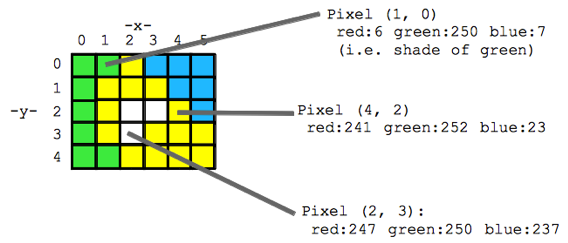
Think of an image as a spread sheet, where each cell is a pixel and each pixel is assigned a value (Fig. 2). Each value is associated with a color and when the sheet is zoomed out and viewed as a whole, the image comes together. In color imagery, which is also referred to as RGB, each pixel is associated with the values of the three color bands (red, green, and blue) that make up that color. In a thermal image, each pixel’s value is a temperature value. Thinking about an image as a grid of values is helpful to understand the challenge of translating the larger patterns we see into something the computer can interpret. In image analysis this process can involve using the values of the pixels themselves or the relationships between the values of neighboring pixels.
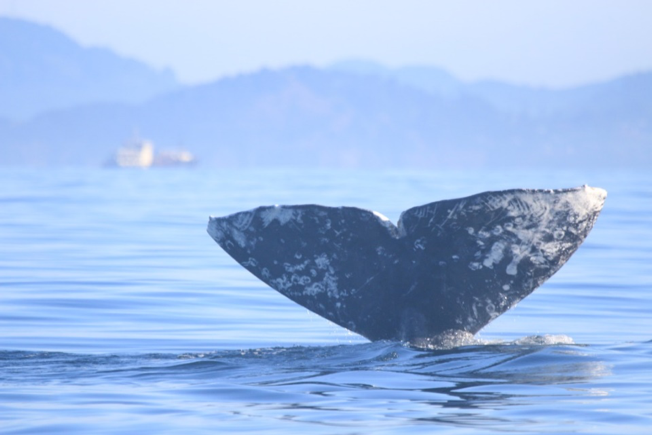
Our brains take in the whole picture at once and we are good at identifying the objects and patterns in an image. Take Figure 3 for example: an astute human eye and brain can isolate and identify all the different markings and scars on the fluke. Yet, this process would be very time consuming. The trick to building an algorithm to conduct this work is figuring out what processes or tools are needed to get a computer to recognize what is marking and what is not. This iterative process is the algorithm development.

Development
An image analysis algorithm will typically involve some sort of thresholding. Thresholds are used to classify an image into groups of pixels that represent different characteristics. A threshold could be applied to the image in Figure 3 to separate the white color of the markings on the fluke from the darker colors in the rest of the image. However, this is an oversimplification, because while it would be pretty simple to examine the pixel values of this image and pick a threshold by hand, this threshold would not be applicable to other images. If a whale in another image is a lighter color or the image is brighter, the pixel values would be different enough from those in the previous image for the threshold to inaccurately classify the image. This problem is why a lot of image analysis algorithm development involves creating parameterized processes that can calculate the appropriate threshold for each image.
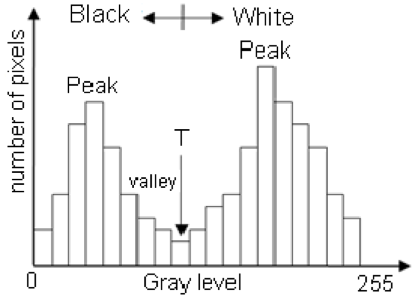
One successful method used to determine thresholds in images is to first calculate the frequency of color in each image, and then apply the appropriate threshold. Fletcher et al. (2009) developed a semiautomated algorithm to detect scars in seagrass beds from aerial imagery by applying an equation to a histogram of the values in each image to calculate the threshold. A histogram is a plot of the frequency of values binned into groups (Fig. 4). Essentially, it shows how many times each value appears in an image. This information can be used to define breaks between groups of values. If the image of the fluke were transformed to a gray scale, then the values of the marking pixels would be grouped around the value for white and the other pixels would group closer to black, similar to what is shown in Figure 4. An equation can be written that takes this frequency information and calculates where the break is between the groups. Since this method calculates an individualized threshold for each image, it’s a more reliable method for image analysis. Other characteristics could also be used to further filter the image, such as shape or area.
However, that approach is not the only way to make an algorithm applicable to different images; semi-automation can also be helpful. Semi-automation involves some kind of user input. After uploading the image for analysis, the user could also provide the threshold, or the user could crop the image so that only the important components were maintained. Keeping with the fluke example, the user could crop the image so that it was only of the fluke. This would help reduce the variety of colors in the image and make it easier to distinguish between dark whale and light marking.
Why algorithms are important
Algorithms are helpful because they make our lives easier. While it would be possible for an analyst to identify and digitize each individual marking from a picture of a gray whale, it would be extremely time consuming and tedious. Image analysis algorithms significantly reduce the time it takes to process imagery. A semi-automated algorithm that I developed to count penguins from still drone imagery can count all the penguins on a one km2 island in about 30 minutes, while it took me 24 long hours to count them by hand (Bird et al. in prep). Furthermore, the process can be repeated with different imagery and analysts as part of a time series without bias because the algorithm eliminates human error introduced by different analysts.
Whether it’s a simple combination of a few processes or a complex series of equations, creating an algorithm requires breaking down a task to its most basic components. Development involves translating those components step by step into an automated process, which after many trials and errors, achieves the desired result. My first algorithm project took two years of revising, improving, and countless trials and errors. So, whether creating an algorithm or working to understand one, don’t let the jargon nor the endless trials and errors stop you. Like most things in life, the key is to have patience and take it one step at a time.
References
Bird, C. N., Johnston, D.W., Dale, J. (in prep). Automated counting of Adelie penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae) on Avian and Torgersen Island off the Western Antarctic Peninsula using Thermal and Multispectral Imagery. Manuscript in preparation
Fletcher, R. S., Pulich, W. ‡, & Hardegree, B. (2009). A Semiautomated Approach for Monitoring Landscape Changes in Texas Seagrass Beds from Aerial Photography. https://doi.org/10.2112/07-0882.1
Moallem, Payman & Razmjooy, Navid. (2012). Optimal Threshold Computing in Automatic Image Thresholding using Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization. Journal of Applied Research and Technology. 703.









































You must be logged in to post a comment.